Topic: Equilibrium, Test No.: 02, Total MCQs: 15
Congratulations - you have completed Topic: Equilibrium, Test No.: 02, Total MCQs: 15.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
In a reversible chemical reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of any one of the reactants is doubled, then the equilibrium constant will [West Bengal JEE 2012]
also be doubled | |
be halved | |
remain the same | |
become one-fourth |
Question 2 |
In 1L saturated solution of AgCl[KSP(AgCl) = 1.6 × 10–10], 0.1 mol of CuCl [KSP(CuCl) = 1.0 × 10–6] is added.
The resultant concentration of Ag+ in the solution is 1.6 × 10–x. The value of "x" is. [IIT JEE 2011]
7 | |
9 | |
13 | |
15 |
Question 3 |
One dm3 solution containing 10–5 moles each of Cl– ions and CrO4–2 ions is treated with 10–4 mole of silver nitrate. Which one of the following observations is made? [Karnataka CET 2010]
[KSPAg2CrO4 = 4 × 10–12]
[KSP AgCl = 1 × 10–10]
Silver chromate gets precipitated first. | |
Precipitation does not occur. | |
Both silver chromate and silver chloride start precipitating simultaneously. | |
Silver chloride gets precipitated first. |
Question 4 |
In aqueous solution the ionisation constants for carbonic acid are
K1 = 4.2 × 10–7 and K2 = 4.8 × 10–11
Select the correct statement for a saturated 0.034 M solution of the carbonic acid. [AIEEE 2010]
The
concentration of H+ is double that of | |
The
concentration of | |
The
concentration of | |
The
concentrations of H+ and |
Question 5 |
Three reactions involving 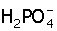 are given below:
[AIEEE 2010]
are given below:
[AIEEE 2010]
(i) H3PO4 + H2O → H3O+ + 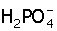
(ii) 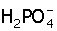 + H2O →
+ H2O → 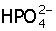 H3O+
H3O+
(iii) 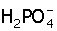 + OH− → H3PO4 + O2+
+ OH− → H3PO4 + O2+
In which of the above does 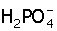 act as an acid?
act as an acid?
(i) only | |
(ii) only | |
(i) and (ii) | |
(iii) only |
Question 6 |
Solubility product of silver bromide is 5.0 × 10–13. The quantity of potassium bromide (molar mass taken as 120 g mol–1) to be added to 1 litre of 0.05 M solution of silver nitrate to start the precipitation of AgBr is [AIEEE 2010]
5.0 × 10–8 g | |
1.2 × 10–10 g | |
1.2 × 10–9 g | |
6.2 × 10–5 g |
Question 7 |
Solid Ba(NO3)2 is gradually
dissolved in a
1.0 × 10–4 M Na2CO3 solution. At what
concentration of Ba2+ will a precipitate begin to form? [AIEEE
2009]
(Ksp for BaCO3 = 5.1 × 10–9)
5.1 × 10–5 M | |
8.1 × 10–8 M | |
8.1 × 10–7 M | |
4.1 × 10–5 M |
Question 8 |
At 25°C, the solubility product of Mg(OH)2 is 1.0 × 10–11. At which pH, will Mg2+ ions start precipitating in the form of Mg(OH)2 from a
solution of 0.001 M Mg2+ ions? [AIEEE 2010]
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 |
Question 9 |
The equilibrium constants ![]() for the reactions
X
for the reactions
X ![]() 2Y and
Z
2Y and
Z ![]() P + Q,
respectively are in the ratio of 1 : 9. If the degree of dissociation of X
and Z be equal then the ratio of total pressure at these equilibria is [AIEEE
2008]
P + Q,
respectively are in the ratio of 1 : 9. If the degree of dissociation of X
and Z be equal then the ratio of total pressure at these equilibria is [AIEEE
2008]
1 : 36 | |
1 : 1 | |
1 : 3 | |
1 : 9 |
Question 10 |
Three moles of PCl5, three moles of PCl3 and two moles of Cl2 are taken in a closed vessel. If at equilibrium the vessel has 1.5 moles of PCl5, the number of moles of PCl3 present in it is [Karnataka CET 2008]
5 | |
3 | |
6 | |
4.5 |
Question 11 |
For the reaction 2HI(g) ![]() H2(g) + I2(g)
– QKJ, the equilibrium constant depends upon [Karnataka CET 2008]
H2(g) + I2(g)
– QKJ, the equilibrium constant depends upon [Karnataka CET 2008]
temperature | |
pressure | |
catalyst | |
volume |
Question 12 |
N2 + 3H2 ![]() 2NH3 +
heat.
2NH3 +
heat.
What is the effect of the increase of temperature on the equilibrium of the reaction? [Karnataka CET 2008]
equilibrium is shifted to the left | |
equilibrium is shifted to the right | |
equilibrium is unaltered | |
reaction rate does not change |
Question 13 |
Four species are listed below
(i) 
(ii) H3O+
(iii) 
(iv) HSO3F
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of their acid strength? [AIEEE 2008]
iv < ii < iii < i | |
ii < iii < i < iv | |
i < iii < ii < iv | |
iii < i < iv < ii |
Question 14 |
The first and second dissociation constants of an
acid H2A are
1.0 × 10−5 and 5.0 × 10−10 respectively.
The overall dissociation constant of the acid will be [AIEEE 2007]
5.0 × 10−5 | |
5.0 × 1015 | |
5.0 × 10−15 | |
0.0 × 105 |
Question 15 |
Phosphorus pentachloride dissociates as follows, in
a closed reaction vessel,
PCl5(g) ![]() PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
If total pressure at equilibrium of the reaction mixture is P and degree of dissociation of PCl5 is x, the partial pressure of PCl3 will be [AIEEE 2006]
| |
| |
| |
|






